나토 확장이 이제 마지막 관문을 남겨둔 상태다,
딱 러시아 한 나라만 남았다.
그리고 푸틴 대통령은 휘하 군부세력이 서로 다투는,
민망하고 절망적인 상황을 관리해야 하는 절박함에 봉착했다.
앞으로 러시아는 어찌해야 하나?
나토 회원국으로 자발적으로 참가해야 하나, 아니면
나토와 대척하면서, 다시 힘을 키워야 하나?
러시아 확장, 왜 이 정도까지 추진되었는지, 살펴본다.
->나토는 왜 창설되었나?
냉전 시대의 유물이다, 나토와 바르샤바 조약기구와 맞설 때
창설되었다. 그리고 구소련이 무너지면서, 바르샤바 조약기구는
해체되었고, 나토는 해체되지 않고 그대로 유지되어 오고 있다.
->나토가 해체되지 않은 이유는?
굳이 말하자면, 러시아가 아직 건재하기 때문이다.
구소련체제에 억눌렸던 동유럽 국가들이 모두 나토 회원국으로
참가하면서, 사실상 새로운 안보기구로 재탄생할 수 있었으나,
러시아가 나토에 반발하며 버티면서, 나토의 생존력을 강화시켜줬다.
->만일 러시아가 나토 회원국이 되면?
나토의 이상과 목표가 실현되겠고, 이렇게 되면,
나토가 새로운 형태의 안보기구로 재탄생할 수 있다.
유럽전체가 하나의 목표와 이상으로 결성된 상태가 되고,
지정된 적대국가가 없는 상태이므로, 집단동맹이 아니라,
집단안보기구 성격으로 바뀔 수 있다.
**나토의 확장 과정
아래 그림에서처럼, 나토는 냉전체제가 해체된 이후,
유럽 전역을 아우르는 포괄적 집단동맹으로 발전했다.
특히 초록색, 파란색 계열 국가들이
구소련 해체 이후 나토 회원국으로 크게 증가했다.
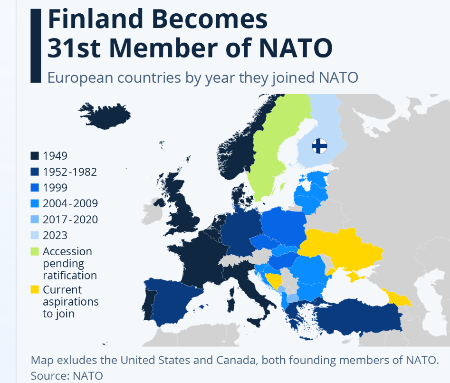
**아시아는 나토처럼 안되나?
과거 구소련이 아시아 전체를 아우르는 지역안보기구를 창설하자고
적극적이었다.
하지만 미국은 유럽에서처럼 집단안보동맹이 아니라,
세력균형 질서를 더 선호한다.
미국이 강력한 군사력을 앞세워 중국과 러시아를 봉쇄할 수 있다고
믿을 뿐 아니라, 지역 집단안보동맹은 서로 적대적인 국가들이 모여서
결성될 수 없다고 생각하기 때문이다.
아시아에서 나토와 같은 집단동맹이 체결된다면,
여기에 참여할 대상국가는,
미국+일본+한국+호주+뉴질랜드+필리핀+a
정도로 생각할 수 있다,
만일 이런 집단동맹이 출범하면, 유럽의 나토처럼, 동남아국가들을
상대로 확장 엔진을 가동시킬 수 있다.
이렇게 되면, 한국이 지금보다는 더 유리한 안보여건을
형성할 수도 있다.
**참고자료; NATO 확장 일지 (AP, May10 2022)
1949: The North Atlantic Treaty Organization is founded to deter Soviet expansion and a revival of European militarism. The 12 original members are the United States, Canada, Britain, Belgium, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway and Portugal.
1955: West Germany joins NATO. In response, the Soviet Union and seven countries in Eastern Europe form the eight-nation Warsaw Pact.
1982: Spain becomes the 16th member of NATO.
1991: The Soviet Union collapses and the Warsaw Pact is dissolved.
1994: Finland and Sweden join NATO’s Partnership for Peace program. The following year they join the European Union, effectively ceasing to be neutral, but remaining military nonaligned.1999: Three former Warsaw Pact nations — the Czech Republic, Hungary and Poland — join NATO.
2001: Article 5 in the NATO treaty, which stipulates that an attack on any NATO member is an attack on all, is triggered for the first time after the 9/11 attacks on the United States.
2002: The NATO-Russia Council is formed to help NATO members and Russia to work together on security issues.
2003: NATO takes command of the International Security Assistance Force in Afghanistan (ISAF).
2004: The biggest NATO expansion to date as seven countries become members: Bulgaria, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. The latter three are the only former Soviet republics to have joined the alliance.
2008: NATO countries welcome Ukraine and Georgia’s aspirations to join the alliance, angering Russia. In August, Russia wins a short war with Georgia over the breakaway regions of South Ossetia and Abkhazia, which Moscow recognizes as independent states.2009: Croatia and Albania become NATO members.
2011: NATO enforces a no-fly zone over Libya. Sweden takes part with fighter jets on reconnaissance missions.
2014: NATO suspends most cooperation with Russia after its annexation of Crimea.
2015: NATO ends the ISAF mission in Afghanistan. The alliance remains in Afghanistan to train local security forces until the Taliban takeover in 2021.
2017: Montenegro joins NATO.
2020: North Macedonia becomes NATO’s 30th member.
'글로벌 시사' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 북중관계 실체, 중국이 남북한을 관리하는 방법 (0) | 2023.07.11 |
|---|---|
| 국제원자력기구 IAEA 유엔 산하기구 맞나? (0) | 2023.07.11 |
| 후쿠시마 오염수 방류, 해상방류가 최상 최적인 이유, IAEA 그로시 사무총장 반론 (0) | 2023.07.10 |
| 후쿠시마 오염수, 농업 공업용수로 사용하면 안될까? (0) | 2023.07.09 |
| 시진핑 리더십, 다시 부활하는 홍위병 광기 (0) | 2023.07.05 |
